Factors Affecting Equilibria
Factors Affecting Equilibria: Overview
This topic covers concepts, such as, Factors Affecting Equilibrium, Le Chatelier's Principle, Application of Le-Chatlier's Principle in Industrial Processes & Simultaneous Equilibria etc.
Important Questions on Factors Affecting Equilibria
Consider the following equilibrium in a closed container
At a fixed temperature, the volume of the reaction container is halved. For this change, which of the following statements holds true regarding the equilibrium constant and degree of dissociation ?
For the chemical reaction , the amount of at equilibrium is affected by –
Standard Gibbs free energy change for isomerisation reaction:
is If more trans-2 pentene is added to the reaction vessel, then:
Consider the following equilibrium in a closed container
At a fixed temperature, the volume of the reaction container is halved. For this change, which of the following statements holds true regarding the equilibrium constant and degree of dissociation ?
In which of the following equilibrium, change in the volume of the system does not alter the number of moles –
The plot of versus for a reversible reaction is shown.
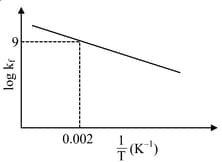
Pre-exponential factors for the forward and backward reactions are and , respectively. If the value of for the reaction at is , the value of at is
equilibrium constant of the reaction, rate constant of forward reaction, rate constant of backward reaction]
The equilibrium constant for this reaction at is and at is . The mean heat of formation of mole of ammonia from its elements in the gives range of temp. is
For the reaction, , which of the following will increase the extent of the reaction at equilibrium?
The thermal dissociation equilibrium reaction of is studied under different conditions
For this equilibrium reaction, the correct statement(s) is/ (are):
At the equilibrium of the reaction, , the number of moles of at equilibrium is affected by the
Which of the following reactions will not get affected on increasing the pressure?
Consider the following reaction in closed container at equilibrium. What would be the effect of addition of on the equilibrium concentration of ?
Water freezes at as
Then by increasing pressure.
On applying pressure to the equilibrium,
Which phenomenon will happen?
Glauber's salt, , was used by J.R.Glauber in the century as a medical agent. At
Which of the following change will take reaction in forward direction?
What is the effect of adding helium gas (at constant volume) to an equilibrium mixture of the reaction?
According to le-Chatelier's principle, adding heat to a solid and liquid in equilibrium will cause the
For a gas phase reaction:
The backward reaction is favoured
By introducing inert gas at constant volume
By introducing inert gas at constant pressure
By adding at constant volume
By adding at constant volume
The correct statements is/are
For the reaction , the forward reaction of constant temperature is favoured by
(1) Introducing an inert gas at constant volume
(2) Introducing chlorine gas at constant volume
(3) Introducing an inert gas at constant pressure
(4) Introducing at constant volume
(5) Introducing gas at constant volume
In which of the following reactions, an increase in the volume of the container will favour the formation of product?
